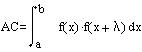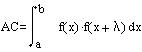Short definitions
- Constitutional descriptors
- Topological descriptors
- BCUT descriptors
- Autocorrelations
- Charge descriptors
The most simple and commmon descriptors, reflecting the molecular composition of
a compuond without any information on its molecular geometry.
Examples of constitutional descriptors are number of atoms, number of bonds, number
of specific atom types, molecular weight, etc.
Descriptors that provide information on the 2d molecular geometry of a compound.
Between the most common topological descriptors are the Wiener index, the
information index on size, etc.
Descriptors represented by the eigenvalues of a square symmetric matrix that
provides information on the molecular graph.
Molecular descriptors based on the autocorrelation function ACf defined as:
Equation 1:Autocorrelation function
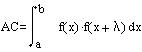 |
where f(x) is any function of the variable x, and lambda is the lag
representing and interval of x; a and b define the whole studied interval
of the function.
For spacial autocorrelations molecular descriptors calculated on a molecular
graph, the lag lambda is defined as the topological distance.
Descriptors that describe the electronic aspect of both the complete molecule,
and of particular regions.
Electrical charges in the molecule are the driving force of electrostatic
interactions, and it is well known that local electron densities or charges
play a fundamental role in many chemical reactions, physico-chemical properties and
receptor-ligand binding affinity.
Copyright (c) Vladimir Josef Sykora and Morphochem AG 2003